34 view of contents in Thoracic Cavity without visual interference Biology Diagrams Learn about the thoracic cavity, the second largest hollow space of the body, that contains the lungs, heart, and esophagus. Find out how diseases such as pleurisy, pneumothorax, and chylothorax affect the pleura and the pleural cavity.

Learn about the thorax, the area of the body between the neck and the abdomen, and its bony, muscular and organ structures. The thoracic cavity contains the lungs, the heart, the thymus gland and the breasts, as well as the great vessels associated with the heart. The thorax is divided into bony structures, muscles, vessels, nerves, and the thoracic cavity.Below is a detailed breakdown of its anatomy: Boundaries of the Thorax. The thorax has defined anatomical boundaries: Superior Boundary: Thoracic inlet (or superior thoracic aperture) at the base of the neck.; Inferior Boundary: Diaphragm, separating the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity.

Thoracic Cavity: Location and Function Biology Diagrams
Thoracic wall The first step in understanding thorax anatomy is to find out its boundaries. The thoracic, or chest wall, consists of a skeletal framework, fascia, muscles, and neurovasculature - all connected together to form a strong and protective yet flexible cage.. The thorax has two major openings: the superior thoracic aperture found superiorly and the inferior thoracic aperture

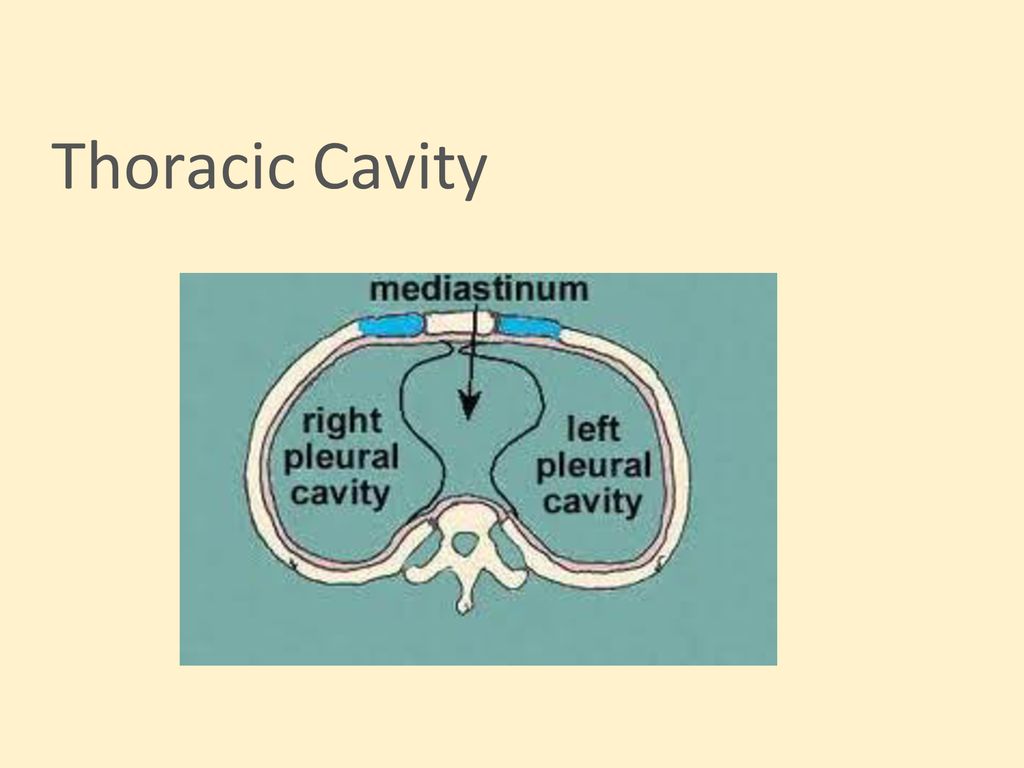
Learn about the thoracic cavity, a cavity of vertebrates that contains the heart, lungs, and other vital organs. Find out how the thoracic cavity is bounded, protected, and connected to other cavities and systems. Atlas of Anatomy 6 Thoracic Cavity. Divisions of the Thoracic Cavity. The thoracic cavity is divided into three large spaces: the mediastinum (p. 76) and the two pleural cavities (p. 102). Fig. 6.1 Thoracic cavity Coronal section, anterior view. Fig. 6.2 Divisions of the mediastinum. Fig. 6.3 Transverse sections of the thorax
Anatomy, Thorax Biology Diagrams
The thoracic cavity is found deep in the thoracic wall, superior to the diaphragm, and inferior to the root of the neck (thoracic aperture). The thoracic cavity contains organs and tissues that function in the respiratory (lungs, bronchi, trachea, pleura), cardiovascular (heart, pericardium, great vessels, lymphatics), nervous (vagus nerve Learn about the thoracic cavity, a space in your chest that contains your heart, lungs and other organs. Find out how it's divided into three parts, what structures it includes and what conditions can affect it. The picture displays the mediastinum on sagittal plane, thoracic diaphragm at the bottom, the heart (cor), behind sternum and ribs (to the left on the picture (this is the anterior/front) and to the right (posterior/back)), you have the thoracic vertebrae.. The thoracic cavity (or chest cavity) is the chamber of the body of vertebrates that is protected by the thoracic wall (rib cage and
