Food Chains Webs and Ecological Pyramids Biology Diagrams The flightless dung beetle occupies an ecological niche: exploiting animal droppings as a food source.. In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition. [1] [2] It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of resources and competitors (for example, by growing when resources are abundant, and when predators, parasites and pathogens
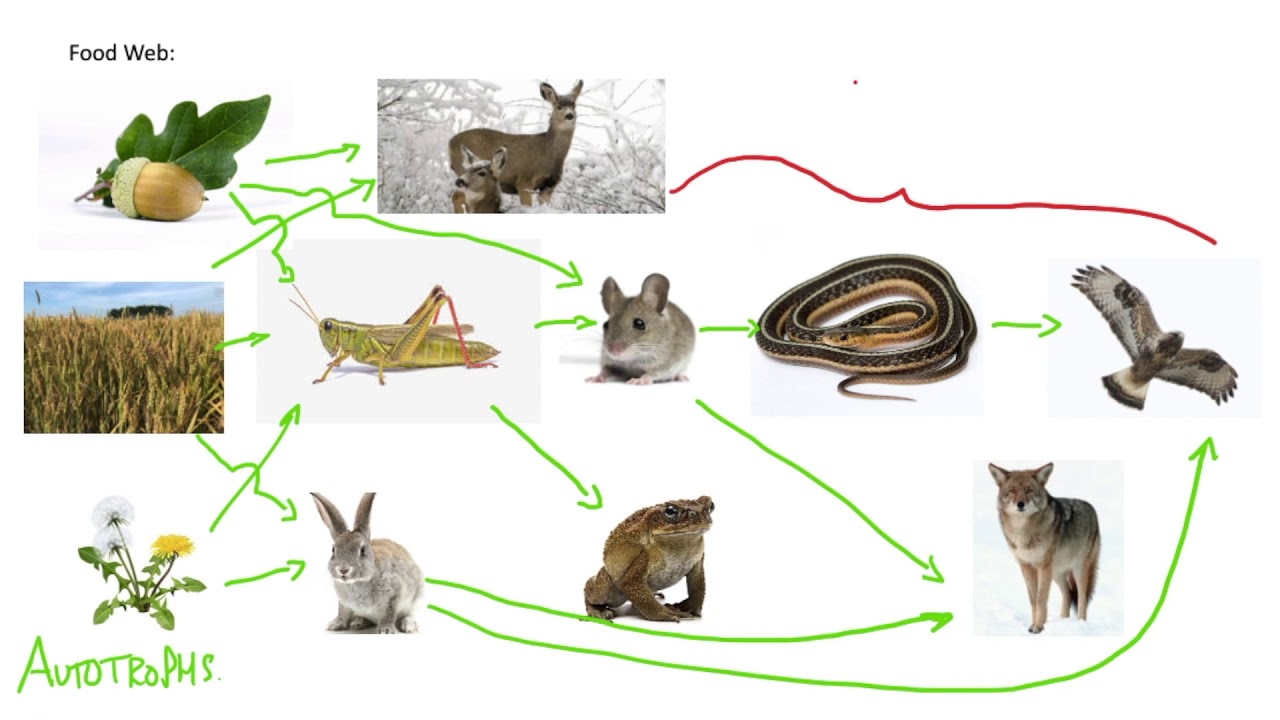
Food chains reveal the relationships between organisms, showing how each organism plays a role in maintaining ecological balance. By studying food chains, ecologists better understand ecosystem dynamics, including the flow of energy, population control, and the impact of human activities on natural habitats.

Ecosystem, Meaning, Structure, Functions, Types, UPSC Notes Biology Diagrams
Each niche contributes uniquely to the web of life, affecting food chains and habitat stability. Exploring aspects such as keystone species, resource partitioning, and trophic level niches enhances our understanding of ecosystem function and adaptation. This exploration reveals the balance that sustains life on Earth. Keystone Species
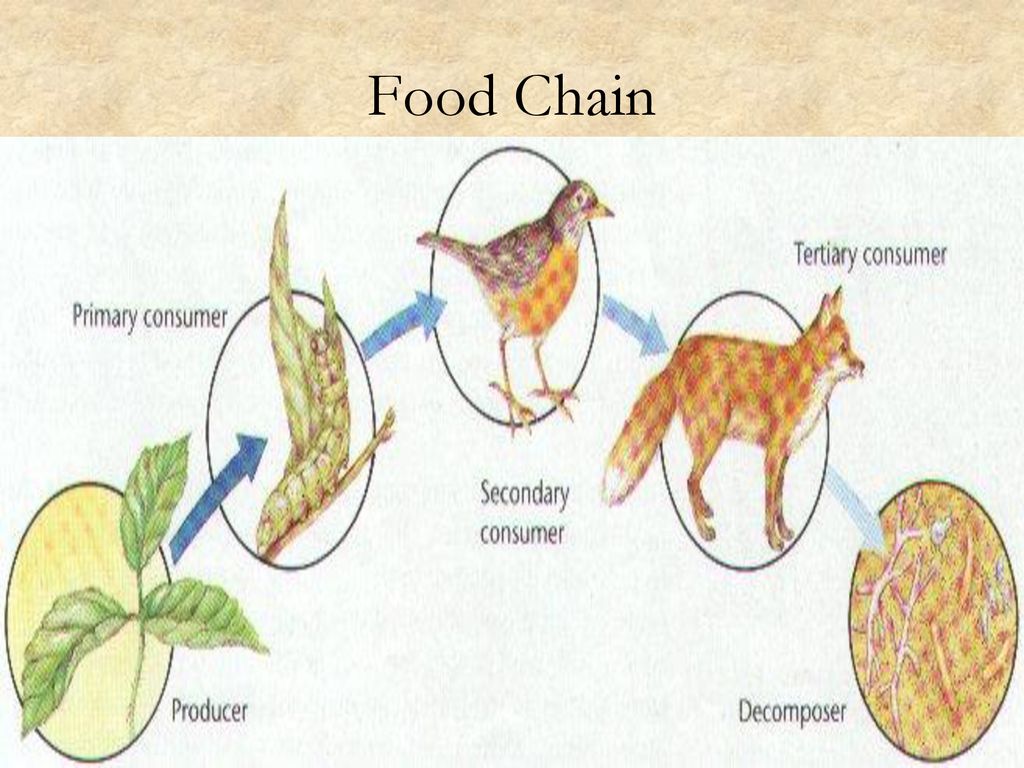
Food chain. The food chain is an ideal representation of flow of energy in the ecosystem. In food chain, the plants or producers are consumed by only the primary consumers, primary consumers are fed by only the secondary consumers and so on. The producers that are capable to produce their own food are called autotrophs. Trophic levels and ecological niches are fundamental concepts in ecology that help explain how organisms interact within their environments. The trophic level defines an organism's position in the food pyramid, which typically consists of primary producers at the base (photosynthetic plants), followed by primary consumers (herbivores), secondary consumers (omnivores), tertiary consumers
Will a large complex model ecosystem be viable? The essential role of ... Biology Diagrams
Importance of Ecological Niche. It permits the coexistence of several species, usually without intense competition and under scarce shared resources. It facilitates species to be aware of their position in the food chain and ecology. The number of niches in an ecosystem defines the number of species present. Thus, they define the variety of the An ecological niche is a term used by ecologists to describe the role a species plays in an ecosystem. The niche is affected by biotic and abiotic factors. Ecological niches are affected by interspecies competition. This leads to competitive exclusion, overlapping niches and resource partitioning. the chain of islands known as the Channel
