Genetic Engineering Info Biology Diagrams Pathway Description: The G2/M DNA damage checkpoint serves to prevent the cell from entering mitosis (M-phase) with genomic DNA damage. Specifically, the activity of the Cyclin B-cdc2 (CDK1) complex is pivotal in regulating the G2-phase transition wherein cdc2 is maintained in an inactive state by the tyrosine kinases Wee1 and Myt1. Although individual components of the G2 phase checkpoint recovery pathway have been shown to have effects on DNA repair in model systems 14,15,16,18, the mechanism by which this dysregulation Analyzing the G2 checkpoint requires precise experimental techniques to assess checkpoint activation, DNA damage response, and cell cycle progression. Flow cytometry is widely used to measure DNA content, distinguishing between G1, S, and G2/M phases. Cells arrested in G2 when the checkpoint is engaged provide a quantifiable readout of its
This checkpoint prevents cells with damaged DNA from entering the M phase, while also pausing so that DNA repair can occur. This regulation is important to maintain genomic stability and prevent cells from undergoing malignant transformation.Ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) and ataxia telangiectasia mutated and rad3 related (ATR) are key G2-M arrest. The G 2-M DNA damage checkpoint is an important cell cycle checkpoint in eukaryotic organisms that ensures that cells don't initiate mitosis until damaged or incompletely replicated DNA is sufficiently repaired. Early signaling proteins in the checkpoint pathway are members of a family of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases,
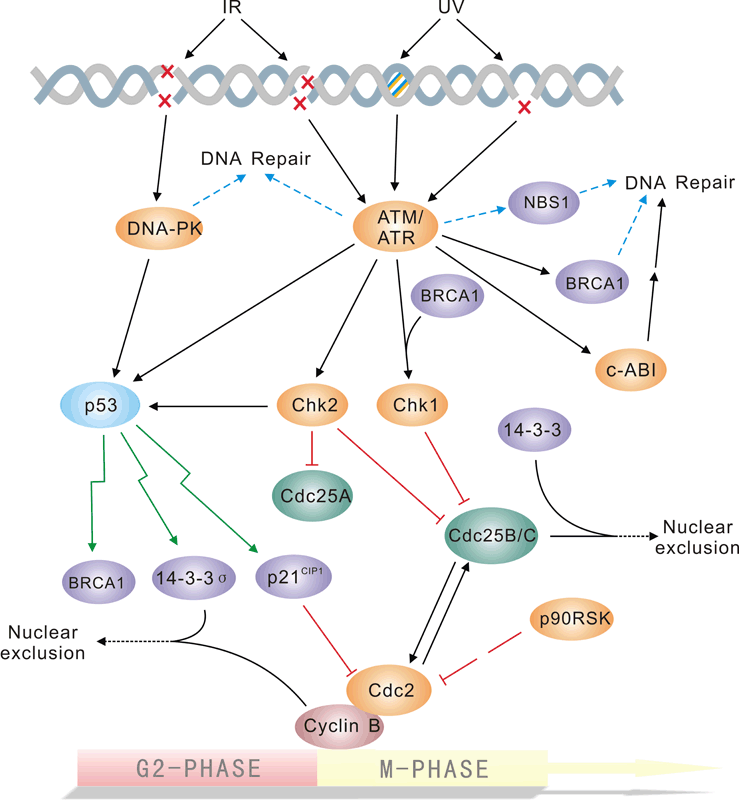
G2M/DNA Damage Checkpoint Biology Diagrams
Cells mount a coordinated response to DNA damage, activating DNA repair pathways and cell-cycle checkpoint pathways to allow time for DNA repair to occur. In human cells, checkpoint responses can be divided into p53-dependent and p53-independent pathways, the latter being predominant in G2 phase of … The G2 DNA damage checkpoint is a complex signaling pathway involving the assembly of several multi-protein complexes, and a phosphorylation cascade leading to Chk1 activation and Cdc2 inhibition. Unal E, et al. DNA damage response pathway uses histone modification to assemble a double-strand break-specific cohesin domain. Mol Cell. 2004 The different DNA damage checkpoints act to inhibit or maintain the inhibition of the relevant CDK that will control the next cell cycle transition. The G2 DNA damage checkpoint prevents mitotic entry solely through T14Y15 phosphorylation of Cdc2 (Cdk1).
